Maximizing Secret Key Extraction from Quantum Cryptographic Systems
Undergraduate Thesis
2021
Abstract
While quantum key distribution (QKD) has been established as a theoretically secure way of sharing secret keys between two remote users who have never had prior communications, it is susceptible to detector-side channel attacks due to imperfect hardware. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (MDI-QKD) systems promise to eliminate all known and unknown detector side-channel attacks and is practical with current technology. This thesis serves as a brief exploration into the intricacies of MDI-QKD.
In this project, a general introduction to QKD in general and MDI-QKD in particular is given, both theoretically and experimentally. Of note is free-space QKD, particularly with satellites, which has been of keen scientific interest of late. Next, a model was progressively built that realistically simulates a general MDI-QKD setup with no assumptions on its implementation parameters. The model was then used to derive several results concerning the performance characteristics of real-world MDI‑QKD systems. Finally, an optimization problem was considered to assist in maximizing key extraction during parameter estimation, a step necessary in the MDI-QKD protocol.
Mathematica
Modeled MDI–QKD setup
MATLAB
Modeled atmospheric distortion and spatial mode mismatch
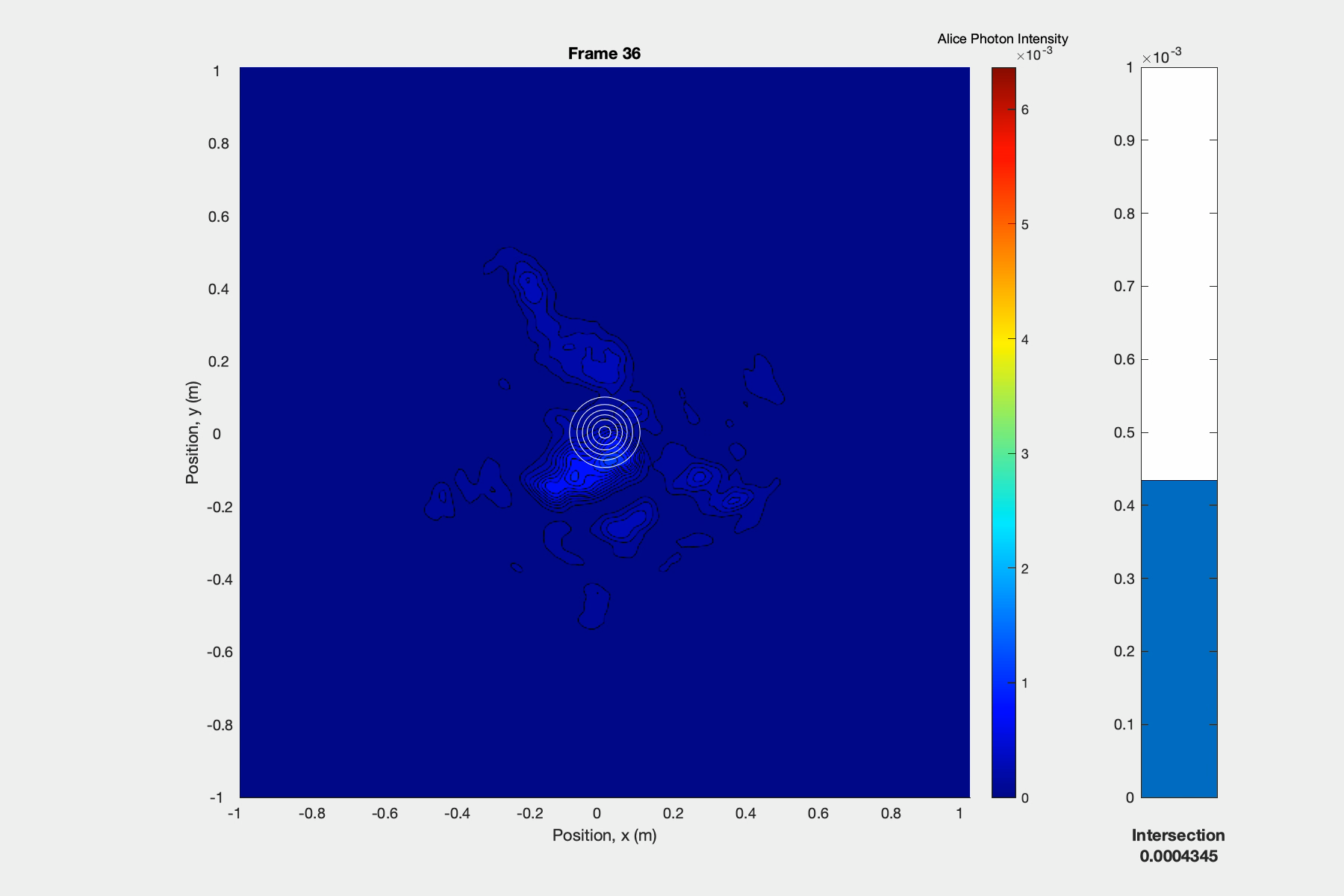
Video
Modeled photon travelled from the satellite through atmosphere to ground station
This thesis was written as part of PC4199 Honours Project in Physics at the National University of Singapore.